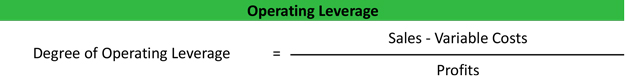
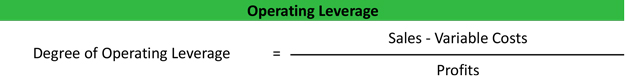
Just like the 1st example we had for a company with high DOL, we can see the benefits of DOL from the margin expansion of 15.8% throughout the forecast period. Despite the significant drop-off in the number of units sold (10mm to 5mm) and the coinciding decrease in revenue, the company likely had few levers to pull to limit the damage to its margins. As a company generates revenue, operating leverage is among the most influential factors that determine how much of that incremental revenue actually trickles down to operating income (i.e. profit). High operating leverage means that small changes in sales can lead to significant changes in operating income. This can be beneficial when sales are increasing but risky when sales are declining. As said above, we can verify that a positive operating leverage ratio does not always mean that the company is growing.
Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
The degree of operating leverage calculator spreadsheet is available for download in Excel format by following the link below. High operating leverage can be risky for a company in several ways, including reduced flexibility, magnified effects of revenue changes, financial risk, and strategic risk. This information shows that at the present level of operating sales (200 units), the change from this level has a DOL of 6 times.


What is your current financial priority?
Similarly, a lower degree of operating leverage indicates that a business has a higher cost of variable ratio. Companies with low DOL will have low fixed expenses and more variable costs, which increases the operating profits. The management of XYZ Ltd. wants to calculate the current degree of operating leverage of its company. Here, the variable cost per unit is Rs.12, while the total fixed cost is Rs.1,00,000.
Example Calculation of DOL
- Finally, it is essential to have a broad understanding of the business and its financial performance.
- If fixed costs are higher in proportion to variable costs, a company will generate a high operating leverage ratio and the firm will generate a larger profit from each incremental sale.
- A high DOL means that a company’s operating income is more sensitive to sales changes.
Let us take the example of Company A, which has clocked sales of $800,000 in year one, which further increased to $1,000,000 in year two. In year one, the operating expenses stood at $450,000, while in year two, the same went up to $550,000. The operating margin in the base case is 50%, as calculated earlier, and the benefits of high DOL can be seen in the upside case. Since 10mm units of the product were sold at a $25.00 per unit price, revenue comes out to $250mm. Common examples of industries recognized for their high and low degree of operating leverage (DOL) are described in the chart below. A second approach to calculating DOL involves dividing the % contribution margin by the % operating margin.
What Is the Difference Between Operating Leverage and Financial Leverage?
An example of a company with a high DOL would be a telecom company that has completed a build-out of its network infrastructure. The catch taking your accounts payable paperless behind having a higher DOL is that for the company to receive positive benefits, its revenue must be recurring and non-cyclical.
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
However, the downside case is where we can see the negative side of high DOL, as the operating margin fell from 50% to 10% due to the decrease in units sold. If revenue increased, the benefit to operating margin would be greater, but if it were to decrease, the margins of the company could potentially face significant downward pressure. In practice, the formula most often used to calculate operating leverage tends to be dividing the change in operating income by the change in revenue.
For the particular case of the financial one, our handy return of invested capital calculator can measure its influence on the business returns. My Accounting Course is a world-class educational resource developed by experts to simplify accounting, finance, & investment analysis topics, so students and professionals can learn and propel their careers. Where Contribution Margin is calculated as Sales Revenue minus Variable Costs. A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation. Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs. Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.
The Degree of Operating Leverage (DOL) is a financial metric that measures how a company’s operating income (EBIT) responds to changes in sales volume. It’s like a financial magnifying glass, showing how your fixed and variable costs can amplify changes in sales into larger changes in operating income. If you have a small business, you must calculate the degree of operating leverage to maintain the bookkeeping of transactions.
In the world of finance, the Degree of Operating Leverage is a key metric for assessing a company’s financial resilience and profit potential. Companies with high fixed costs tend to have high operating leverage, such as those with a great deal of research & development and marketing. With each dollar in sales earned beyond the break-even point, the company makes a profit.
